Cyano group is one of the most common functional groups in organic synthesis, and it can be easily converted into other compounds such as carboxylic acid derivatives, aldehydes, ketones, amines and others. Among them, chiral nitriles can be used as key intermediates in the synthesis of some drug molecules such as naproxen, ibuprofen and flurbiprofen. In addition, there are some drug molecules, where the cyano moiety is directly used as the key functional group.
Top chemical journal Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. recently reported that the research group of Southern University of Science and Technology (SUSTech) Department of Chemistry Professor Zhang Xumu had found an efficient and concise synthetic route to the intermediate of vildagliptin and anagliptin. Their paper was selected as the Cover Article and titled “Asymmetric Hydrocyanation of Alkenes without HCN,” while also earning the sobriquet of “Hot Paper.”

Based on the importance of chiral nitriles in organic chemistry, the synthesis of such compounds has attracted widespread attention from chemists and has led to the development of many methods for the synthesis of chiral nitriles, such as the asymmetric hydrocyanation of olefins and the asymmetric Strecker reaction. However, due to the toxicity and volatility of common cyanating reagents, it is necessary to develop a cyanide-free cyanation reaction.
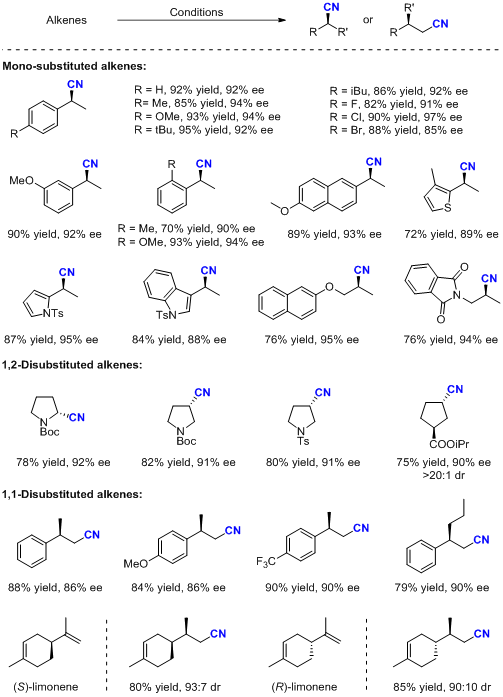
Professor Zhang’s research group used asymmetric hydroformylation, condensation reaction and aza-Cope elimination reaction in sequence to achieve asymmetric hydrocyanation of olefins under cyano-free conditions. Through this strategy, very valuable chiral nitriles can be obtained with high enantioselectivity, yield and generality.

To demonstrate the utility of the reaction, the authors synthesized key chiral intermediates for two drugs, Vidalagliptin (oral antidiabetic, clinically used primarily for the treatment of type 2 diabetes) and annagliptin (Anagliptin, for the treatment of type 2 diabetes). In addition, the group also showed that chiral nitriles could be converted into the corresponding chiral carboxylic acid and primary amine compounds. Their experiments have proved that the reaction has potential application in drug synthesis and organic synthesis.
Li Xiuxiu and You Cai from Zhang’s lab are listed as the first authors of the thesis, and master’s student Zhang Dequan is the fifth author of the thesis. Sustech is the first corresponding unit.
The research received funding from the Shenzhen Science and Technology Innovation Committee, Shenzhen Nobel Prize Scientists Laboratory Project, National Natural Science Foundation of China, SZDRC Discipline Construction Program, and Natural Science Foundation of Hubei Province. The authors would also like to thank SUSTech for their support of their research.
Link to the paper: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/anie.201906111
Proofread ByXia Yingying
Photo ByDepartment of Chemistry