Programmed cell death and caspase proteins play a pivotal role in the host’s innate immune response in combating pathogen infections. Blocking cell death is employed by many bacterial pathogens as a universal virulence strategy. CopC family type III effectors, including CopC from an environmental pathogen Chromobacterium violaceum, utilize calmodulin (CaM) as a co-factor to inactivate caspases by arginine ADPR deacylization. However, the molecular basis of the catalytic and substrate/co-factor binding mechanism is unknown.
Associate Professor Yang Fu’s research group from the School of Medicine at the Southern University of Science and Technology (SUSTech) has collaborated with Professor Shan Li’s research group from Huazhong Agriculture University (HZAU) to determine successive cryo-EM structures of CaM-CopC-caspase-3 ternary complex. The study offers a structural framework for understanding the molecular basis of arginine ADPR-deacylization catalyzed by the bacterial T3SS.
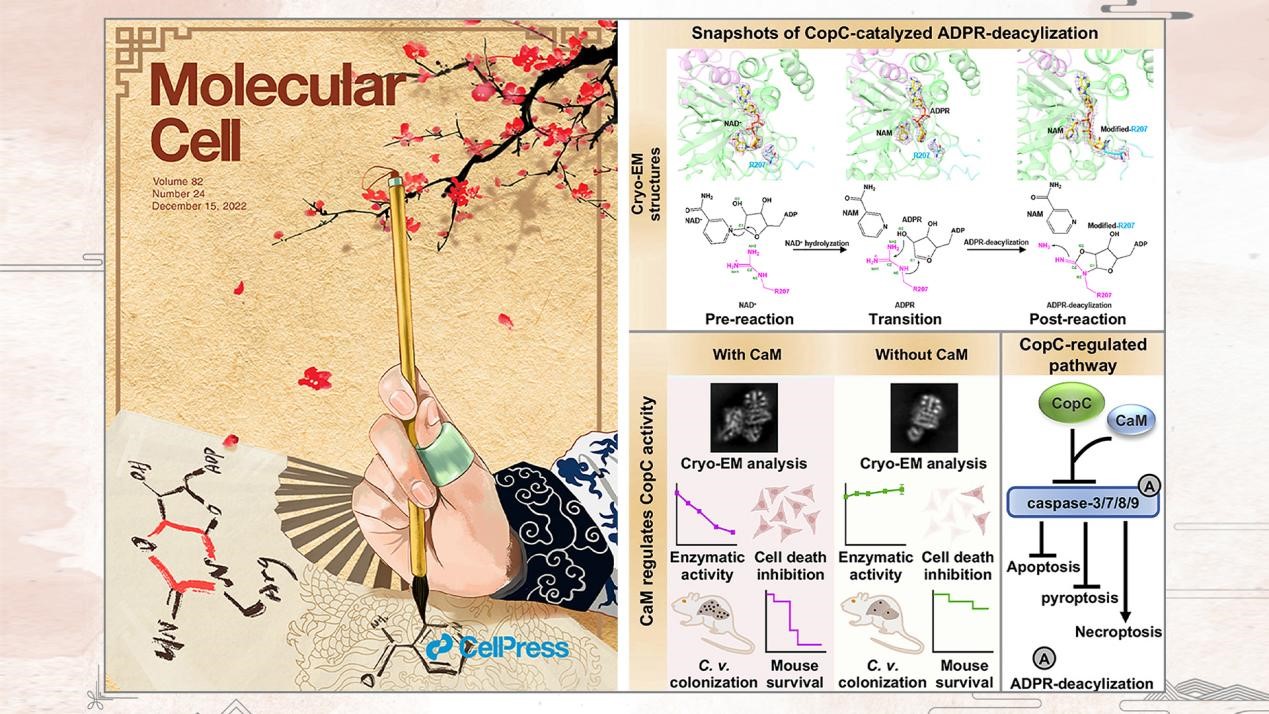
Their article, entitled “Structural insights into caspase ADPR deacylization catalyzed by a bacterial effector and host calmodulin,” has been published in Molecular Cell, and used as the cover story of the current issue.
This study uncovered the catalytic and substrate/co-factor binding mechanisms of CopC family-catalyzed arginine ADPR-deacylization on host caspases. This ancient Chinese ink painting depicted the regulatory effect of co-factor CaM (the jade thumb ring) that enables CopC (the hand) to obtain the ability of catalyzation, which regulates programmed cell death. The ring on thumb entitles the power to change the fate of cells, and the ADPR-deacylization modification was drawn on this thesis. These structural insights are validated by mutagenesis analyses of CopC-mediated ADPR deacylization in vitro and animal infection in vivo. Their study offers a structural framework for understanding the molecular basis of arginine ADPR deacylization catalyzed by the CopC family.
Dr. Kuo Zhang and Dr. Miao Tian of Assoc. Prof. Yang Fu’s research group from the School of Medicine at SUSTech, and Ting Peng and Xinyuan Tao, doctoral students of Prof. Shan Li’s research group at HZAU, are the co-first authors of this paper. Prof. Shan Li and Assoc. Prof Yang Fu are the co-corresponding authors. SUSTech is the first affiliation of the paper.
This study was supported by the National Key Research and Development Programs of China, National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC), HZAU-AGIS Cooperation Fund, and Shenzhen Science and Technology Program.
Paper link: https://www.cell.com/molecular-cell/fulltext/S1097-2765(22)01060-7#secsectitle0010
To read all stories about SUSTech science, subscribe to the monthly SUSTech Newsletter.
Proofread ByAdrian Cremin, Yingying XIA
Photo By