The Cryo-Electron Microscopy Center (Cryo-EM Center) of the Southern University of Science and Technology (SUSTech) has recently been involved in groundbreaking research. Scientists in the Cryo-EM Center have assisted in important research that has been published in both Science and Nature Microbiology. These research papers have broken new ground in scientist’s understanding of mitochondria and influenza.
Cellular processes must respond to change, often by speeding up, slowing down, or stopping altogether. Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) synthases use a transmembrane proton gradient to produce ATP, but this reaction can go in reverse and needs to be halted when conditions are unfavorable. Recently, the Cryo-EM Center took part in research by a team led by Professor Yang Maojun from the School of Life Sciences at Tsinghua University. The paper, published in top academic journal Science, was titled “Cryo-EM structure of the mammalian ATP synthase tetramer bound with inhibitory protein IF1.” It sought to determine the structure of mammalian ATP synthase tetramer using the SUSTech Cryo-Electron Microscope.

This paper focused on the most complete structure of mammalian ATP synthase, and the position and function of each subunit in the complex. ATP synthase monomer is composed of 19 different subunits and 30 proteins. The newly identified subunits are mostly encapsulated in the intermediate region of ATP synthase tetramer, meaning that only in the tetramer protein can all the subunits be contained. The structure of ATP synthase in higher mammals was analyzed, providing an important experimental and structural basis for treating metabolic and neurodegenerative diseases. The research team will continue to study the mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation system in depth, and will devote itself to the development of new targeted drugs for mitochondrial abnormalities.
Link to the paper: https://science.sciencemag.org/content/364/6445/1068
Scientists in the Cryo-EM Center also contributed to a recently published paper that has helped researchers understand more about the influenza D virus polymerase, the fourth of the four major influenza strains. The paper was published in Nature Microbiology under the title, “Structural Insight into RNA Synthesis by influenza D Polymerase.”
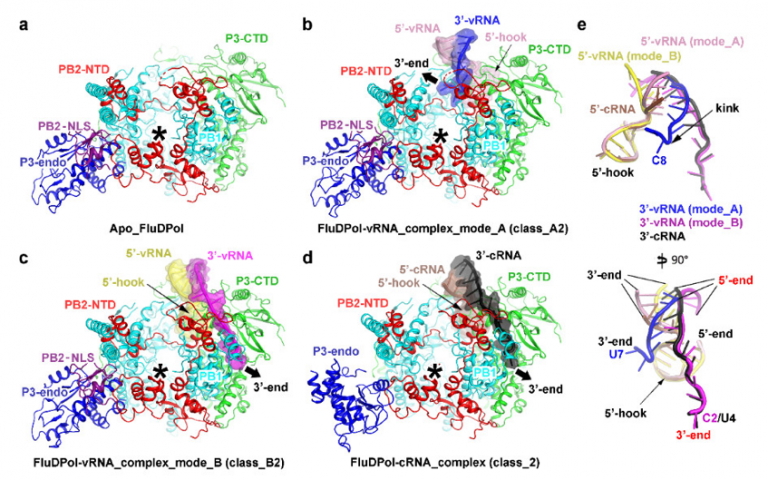
The researchers have provided the structural basis for the different behaviors of influenza virus RNA synthesis and proposed a delicate regulatory mechanism for the production of different RNA species during both transcription and replication. They also identified some key residues regulating these processes, which are conserved across all four influenza strains which indicate that the mechanism might be shared by all influenza viruses. Their findings may provide new clues for the development of broad-spectrum anti-influenza drugs and therapeutics.
Link to the paper: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41564-019-0487-5
The progress of these researches has been strongly supported by the Cryo-EM Center. With the full support of the Development and Reform Commission of Shenzhen Municipality, SUSTech has taken the lead in building the largest cryo electron-microscopy center in mainland China, and the one of the top three cryo-electron microscopy centers in the world. The SUSTech Cryo-Electron Microscopy Center supports high-end biomedical research in SUSTech, Shenzhen, and the Greater Bay Area by providing high quality outputs quickly and efficiently. In just seven months since its official opening, the Cryo-EM Center has had results from its facilities published in top academic journals, reflecting the vigorous, enterprising, flexible and innovative spirit of SUSTech and Shenzhen.
Proofread ByXia Yingying
Photo ByCryo-Electron Microscopy Center